The previous introductory tutorial explained the reasons for choosing the Debian system instead of the CentOS system and some points of complaining. In this article, I want to talk about the choice of the system, common commands, and some basic, my own commonly used editors The device is a bit long, but it's definitely dry stuff.

System selection and installation
Debian packages have a series of prefixes or suffixes, such as in the default download https://www.debian.org/downloadlocation debian-11.0.0-amd64-netinst.iso. in,
-
11 represents the big version is 11, the code name is bullseye, and the code names of each version are derived from the character names in the movie "Toy Story";
-
amd64 means that the system is 64-bit, i386 or x86 is 32-bit, amd64 or x86-64 is 64-bit, and 32-bit systems have been gradually deprecated and are currently only used in specific industries;
-
netinst is a network installation version, just an installer, the installation process requires networking, and the DVD suffix is the full version (such as: debian-11.0.0-amd64-DVD-1.iso), if the system is too large, it will be behind the DVD Add a number, the default DVD-1 is the full version, and the number after that is the software source/package;
-
Firmware prefixes contain third-party non-open source drivers (eg firmware-11.1.0-amd64-DVD-1.iso), including closed-source NIC drivers from companies such as Intel and Realtek.
The full name of VPS is virtual private server (virtual private server). If you need to install a pure version of Debian 11 system, it is recommended to use the Linux one-click reinstallation script of vicer (as follows):
bash <(wget --no-check-certificate -qO- 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MoeClub/Note/master/InstallNET.sh') -d 11 -v 64 -p "自定义root密码" -port "自定义ssh端口"

Common commands
cat Used to view the content of the text file, such as cat /etc/os-release system information will be displayed, as follows:
PRETTY_NAME="Debian GNU/Linux 11 (bullseye)"NAME="Debian GNU/Linux"VERSION_ID="11"VERSION="11 (bullseye)"VERSION_CODENAME=bullseyeID=debianHOME_URL="https://www.debian.org/"SUPPORT_URL="https://www.debian.org/support"BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.debian.org/"
touch Create a new text file, such as touch /home/hello.py a home new Python file under the folder.
ls List all files, but only the most basic files and folders are displayed by default. If you need more detailed information, use ls -lait. This will list all files and folders including hidden files and give the corresponding permissions. , size and date.
cd Enter the specified folder, such as cd /home will enter the homedirectory. The command to return to the upper-level directory is cd .., and the command to return to the directory just operated on is cd -.
mkdir Create a new folder, for example, a new folder mkdir /home/Python will be created home under the Python folder.
mv Moving files and folders can also be used to change the name, such as renaming the above mv /home/hello.py /home/helloworld.py to a subfolder.hello.pyhelloworld.pymv /home/helloworld.py/home/Python/helloworld.pyhelloworld.pyhomePython
cp复制文件, cp /home/Python/hellowrold.py /home/Python/HelloWorld.py will be helloworld.pycopied as HelloWolrd.py. Note: Linux systems are strictly case-sensitive, helloworld.pyand HelloWolrd.pyare two files. If you want to copy the entire folder, you need to take r, that is cp -r, but this command cannot copy hidden folders, you need to use cp -r pathA/. pathB Note that this point .is the soul.
rm Delete, that is, in the legend of the rivers and lakes rm -rf , ris recursive, you can delete the files in the folder, and it fis forced to delete. rm /home/Python/helloworld.py You can delete the helloworld.py file just now, and if you want to delete Python all files including it, yes rm -rf /home/Python .
du -lh Check the size of each file and folder under the current folder. It lis a hard link (a soft link is similar to a shortcut), which his to automatically display the file using K/M/G instead of only K.

Basic text editor nano, vim
One of the big advantages (and disadvantages) of Linux systems is that they do not require GUI by default, so they save a lot of performance costs. The GUI-free version of Debian 11 can start and run normally on a VPS with 512M or even less memory. But the lack of GUI makes it difficult for beginners to modify files. Fortunately, Debian 11 comes with an easy-to-use nano text editor. The following is an example of modifying the update source of the system
nano /etc/apt/sources.list #打开sources.list文件,在Linux系统中,#是注释符,其后的内容会被忽略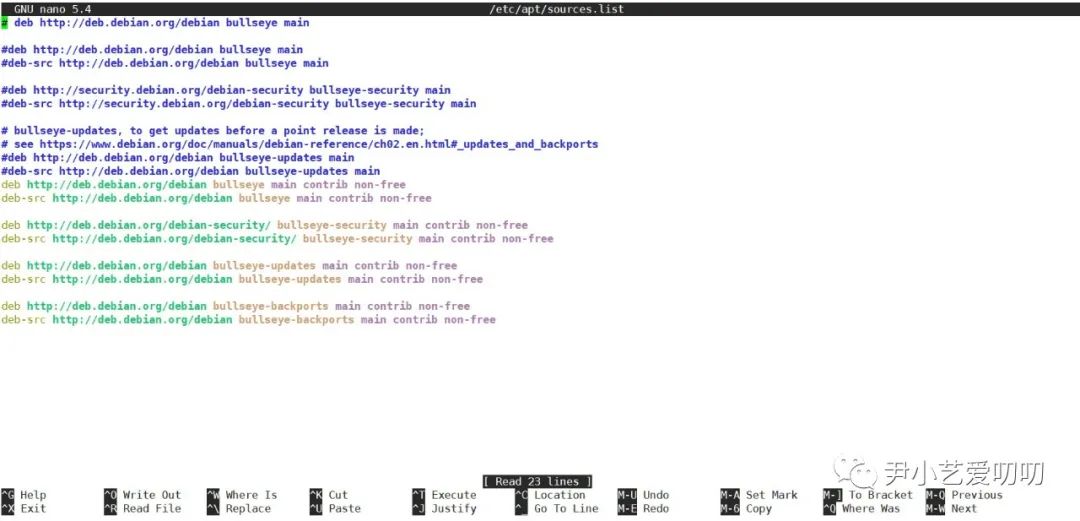
As shown in the figure, it is the interface after nanoopening . The bottom two lines are prompts, such as exit. If the document has been changed, the following figure will appear, asking whether to save. If it has not been changed, it will exit directly.sources.listCtrl+E
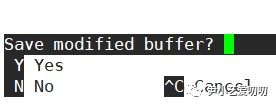
YIf it is saved, it will Nnot be saved, and Ctrl+Cthe operation will be canceled. Input here Y, it will be as follows:

At this point, pressing Enterthe key will save it.
Here is one more sentence about the update source content of Debian 11, which is generally the following 6 lines.
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main contrib non-freedeb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main contrib non-freedeb http://deb.debian.org/debian-security/ bullseye-security main contrib non-freedeb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian-security/ bullseye-security main contrib non-freedeb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates main contrib non-freedeb-src http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye-updates main contrib non-free
deb is represented as a compiled installation package, similar to the MSI installation package on Windows, deb-src is the source file, in case it is not packaged well, it provides the opportunity to compile and install it locally. There are three lines in total. The first line is the system main file, the second line is the security update, and the third line is some update supplements. It is recommended to write all three. There are words at the end of each line main contrib non-free, which mainare officially given packages/sources, which strictly abide by the relevant open source protocols; contribthe packages/sources themselves comply with the relevant open source protocols, but their dependencies are not; they non-freeare proprietary software, such as those mentioned above. to Realtek's WiFi driver, etc. In addition, there is actually Backportsa fourth line, which is transplanted from relatively old software, which is rarely used, and is generally not written by default.
Although nano is good, it has simple functions and is only suitable for some simple text file editing functions, while vim developed from vi has become the god of editors (Emacs is called the editor of gods, and Linus Torvalds, the father of Linux, is using it) . The system will come with vi but not vim, just so we can use the above modified update source to install vim as an example.
Use vim /etc/apt/sources.listOpen to update the source file as shown below:
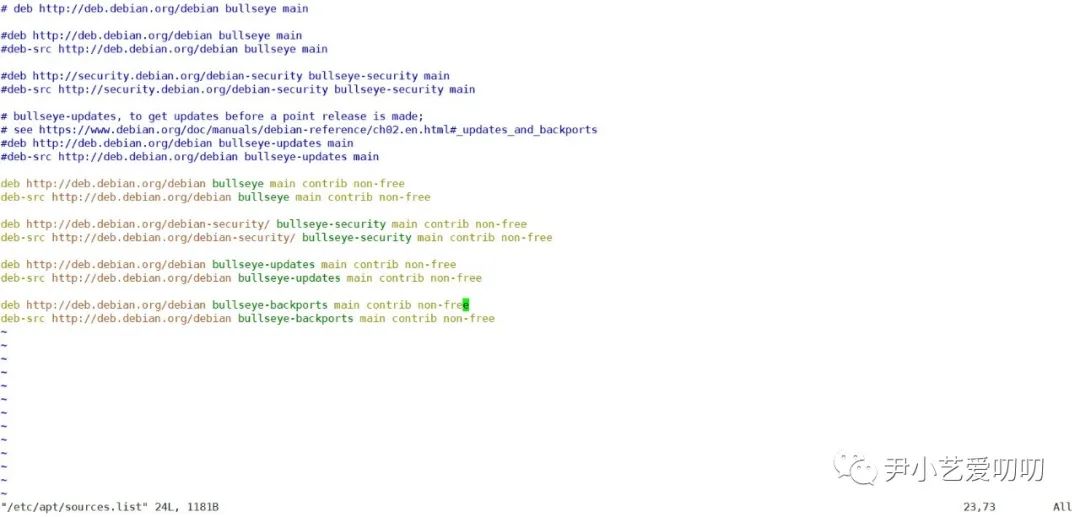
Vim has many functions and is complicated to use, so I have to say it slowly. The lower left corner is the path and name of this file, and the lower right corner is the number of rows and columns of the cursor at this time. At this time, it is not possible to input directly, you must first press insertor ikey to change to insert mode. At this point, the lower left corner is as shown below, and it becomes INSERT/insert mode.

Then it is how to write how to write, some shortcut keys go to Baidu Google Bing, it must be more detailed than me. But it must be mentioned how to save the file: insertpress the esckey (usually the upper left corner of the keyboard, a key that 99% of people may not use very much), INSERT will disappear, as shown below:

At this time, press the :key again, and a colon will appear on the interface, as shown below. Note that this colon is half-width, and full-width colons are useless.

At this time, press wqthese two keys to save the content. w means write/write, q means quit/exit. If you don't want to save, just enter the q key, but sometimes because the file has been modified, vim won't let you exit, q!you can enter it at this time, the exclamation mark means mandatory execution, the file will not be modified after execution and will exit vim.

update system
At this point, whether you use nano or vim, you can edit the update source. Let's take a look at how to update the system and related instructions.
apt updateapt list --upgradableapt upgrade -y
The above three lines are synchronized with the update source, showing which software can be updated and updated.
As above, vim is installed. If you want to uninstall vim, there are the following two commands, either one can be used, but there are differences between them.
apt remove vim -yapt purge vim -y
The first meeting site uninstalls the vim software itself, and the configuration file will still be left; the second one is uninstalled together with the configuration file and related dependencies, so there is a certain risk. In addition, it apt autoremoveis to sort out the entire system, uninstall unnecessary dependencies, and not target specific software.
